Dev.baelanche
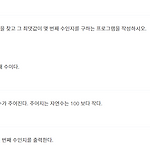
 [백준 6603] 로또
[백준 6603] 로또
중복되지 않으면서 오름차순인 수열을 완전탐색한다. 빈 줄을 끼워넣는 것을 유의한다. public class Main { static int a[]; static int k; static boolean f = true; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st; while(true) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); k = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); if(k == 0) break; a = new int[k..
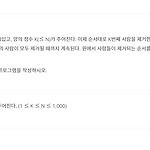 [백준 11866] 조세퍼스 문제 0
[백준 11866] 조세퍼스 문제 0
수열을 q에 담아 K-1번째까지 pop, push를 하며 맨 뒤로 보내주고 K번째 수는 pop 한다. K번째에 pop된 순열을 출력한다. public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); int k = sc.nextInt(); int a[] = new int[n]; Queue q = new LinkedList(); for(int i=1; i
 [백준 4949] 균형잡힌 세상
[백준 4949] 균형잡힌 세상
문자열에서 (, ), [, ] 말고는 신경쓰지 않는다. 1. (, [ 문자는 스택에 바로 담는다. 2. ) 문자는 스택의 top이 (이면 둘이 합쳐서 pop한다. 2-1. ] 문자는 스택의 top이 [이면 둘이 합쳐서 pop한다. 3. ), ] 문자가 들어왔을때 스택이 비어있거나 탑이 자신의 쌍이 아니면 균형이 안잡힌 문자열이다. 4. 문자열 점검이 끝났을때 스택이 비어있어야 한다. public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while(true) { String str = sc.nextLine(); if(str.equals(".")) break; Stack s = new S..
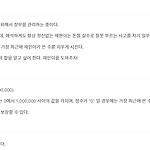 [백준 10773] 제로
[백준 10773] 제로
짱짱 쉬운 스텍 문제이다. 설명은 생략하겠다. public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int k = sc.nextInt(); Stack s = new Stack(); while(k-->0) { int n = sc.nextInt(); if(n != 0) s.push(n); else s.pop(); } int sum = 0; while(!s.isEmpty()) { sum += s.pop(); } System.out.println(sum); } }
 [백준 15685] 드래곤 커브
[백준 15685] 드래곤 커브
이전 세대에 그은 줄을 기억했다가 다음세대에 90도 꺾어서 긋는 방식은 머릿속에서 그려지지가 않았다. 드래곤커브의 순서를 적어봤더니 규칙이 있었다. 시작방향이 0일때의 세대별 방향이다. 선이 이어진대로 +1 하면서 진행되는 규칙을 찾을 수 있었다. x+1 = 4일때는 0으로 바꿔준다. 시작방향에 따른 방향을 정리하고 나머지 부분은 구현만 하면 된다. public class Main { static int a[][] = new int[101][101]; static int direction[][] = new int[4][1024]; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(n..
 [백준 11729] 하노이 탑 이동 순서
[백준 11729] 하노이 탑 이동 순서
재귀함수를 처음 배울때 피보나치 수열과 함께 단골로 등장하는 문제이다. 하노이 탑 풀이 방법을 까먹어서 인터넷을 참고했다. 똑똑한 사람이 너무도 많아 아무데나 검색만 해도 자세한 풀이가 나온다. public class Main { static int cnt = 0; static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); public static void move(int from, int to) { cnt++; sb.append(from + " " + to + "\n"); } public static void hanoi(int n, int from, int by, int to) { if(n == 1) move(from, to); else { hanoi(n-1, from, to,..
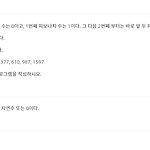 [백준 10870] 피보나치 수 5
[백준 10870] 피보나치 수 5
n이 최대 20이라 문제에 나와있는 점화식을 가지고 재귀하여 풀면 된다. 나는 굳이 탑다운 방식으로 풀었다. public class Main { static int dp[]; public static int f(int k) { if(k == 0) return 0; if(k == 1) return 1; if(dp[k] != -1) return dp[k]; int ret = f(k-1) + f(k-2); dp[k] = ret; return ret; } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); dp = new int[n+1]; Arrays.fill(dp, -1); Syste..